
How and Why Does Skin Age?
Ageing is a natural process that affects every part of the body, and our skin is one of the most visible indicators of this process. With time, our skin undergoes changes that reflect the internal and external factors influencing it. The ageing of the skin can manifest in various ways, including wrinkles, fine lines, loss of elasticity, dryness, and changes in skin tone. Understanding how and why skin ages is essential for maintaining a youthful appearance and knowing how to care for it properly.
The Structure of Skin
Before diving into the aging process, it's essential to understand the basic structure of the skin. The skin is composed of three primary layers:
- Epidermis: The outermost layer that serves as a protective barrier. It contains cells called keratinocytes, which help with the skin's regenerative processes, and melanocytes, which give skin its colour.
- Dermis: Located beneath the epidermis, the dermis contains collagen and elastin, proteins that give skin its strength and elasticity. This layer also houses sweat glands, hair follicles, and blood vessels.
- Subcutaneous Layer (Hypodermis): This is the deepest layer and primarily consists of fat and connective tissues that insulate the body and act as cushioning.

Why Does Skin Age?
Ageing skin is influenced by two primary factors: intrinsic ageing (internal factors) and extrinsic ageing (external factors).
1. Intrinsic Aging
Intrinsic aging refers to the natural, inevitable process of ageing. This process is determined by genetic factors and occurs gradually over time, regardless of external influences. Here's how intrinsic ageing manifests:
-
Collagen Breakdown: Collagen is a key protein in the skin that provides structure and firmness. As we age, our body produces less collagen, leading to sagging skin and the formation of wrinkles. Research suggests that collagen production starts to decline by approximately 1% per year after age 20.
-
Decreased Cell Turnover: In our youth, skin cells regenerate quickly, helping maintain a fresh, glowing complexion. With age, the rate of cell turnover slows down, leading to a buildup of dead skin cells, which contributes to dull and uneven skin tone.
-
Loss of Elastin: Elastin is another important protein that gives skin its ability to snap back after being stretched. Over time, elastin production declines, contributing to sagging and wrinkling.
-
Reduced Oil Production: Sebaceous glands, which are responsible for producing oil, become less active with age, leading to drier skin. This dryness can exaggerate the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
-
Thinning of the Skin: With age, the layers of skin, particularly the dermis, become thinner. This thinning contributes to a loss of plumpness and volume, making skin more fragile and susceptible to damage.
-
Slower Wound Healing: Ageing skin takes longer to repair itself, making it more prone to injury, irritation, and infections.

2. Extrinsic Aging
Extrinsic aging refers to the environmental and lifestyle factors that can accelerate the ageing process. Unlike intrinsic ageing, extrinsic factors can often be controlled or minimised. Here are some of the most common causes:
-
Sun Exposure (Photoageing): The sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays are the primary cause of extrinsic skin aging. UV rays break down collagen and elastin fibers in the skin, leading to wrinkles, loss of elasticity, and pigmentation changes such as age spots. The cumulative effect of sun exposure is known as photoaging, and it can significantly accelerate the visible signs of ageing.
-
Smoking: Smoking constricts blood vessels, reducing oxygen and nutrient delivery to the skin. This can lead to a dull, sallow complexion, while the toxins in cigarettes can damage collagen and elastin, leading to premature wrinkling.
-
Pollution: Environmental pollutants can damage the skin’s protective barrier, contributing to oxidative stress. This accelerates ageing by breaking down collagen and promoting inflammation.
-
Diet: A diet lacking in essential nutrients, particularly antioxidants, can lead to skin damage and accelerated aging. Antioxidants like vitamins C and E help neutralise free radicals that damage skin cells.
-
Repetitive Facial Movements: Habitual facial expressions like squinting or frowning can contribute to the formation of fine lines and wrinkles over time.
-
Stress and Lack of Sleep: Chronic stress and inadequate sleep lead to an increase in cortisol levels, which can break down collagen and result in dull, aged skin. Restorative sleep is crucial for skin regeneration.
How Does Skin Age?
The ageing process involves several key biological changes that occur in the skin’s structure and function. These changes manifest differently depending on whether they result from intrinsic or extrinsic factors.

1. Wrinkles and Fine Lines
Wrinkles are the most noticeable sign of ageing skin. They result from both intrinsic and extrinsic factors. Collagen and elastin break down over time, and skin loses its ability to bounce back, forming lines and creases, especially in areas with repetitive movement (e.g., forehead, around the eyes, and mouth). UV exposure and lifestyle factors like smoking further exacerbate this process.
2. Loss of Elasticity and Sagging
As elastin production declines, skin loses its firmness and elasticity, which leads to sagging. Jowls, drooping eyelids, and loose skin under the chin are common signs of aging. A decrease in fat in the hypodermis also contributes to sagging and a loss of volume in the face.
3. Hyperpigmentation
Uneven skin tone and hyperpigmentation (such as age spots) are common as we age, especially due to sun exposure. UV damage triggers an overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin colour, which leads to the appearance of dark spots.
4. Dryness and Thinning
As oil production decreases, the skin's ability to retain moisture weakens, leading to dryness. Thinning of the epidermis and dermis further reduces the skin's ability to hold onto moisture, exacerbating the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
5. Reduced Blood Circulation
Ageing reduces blood flow to the skin, which means less oxygen and nutrients reach the surface, leading to dullness and slower wound healing.
5 Reasons Dermaplaning at Home is the Ultimate Anti-Ageing Secret
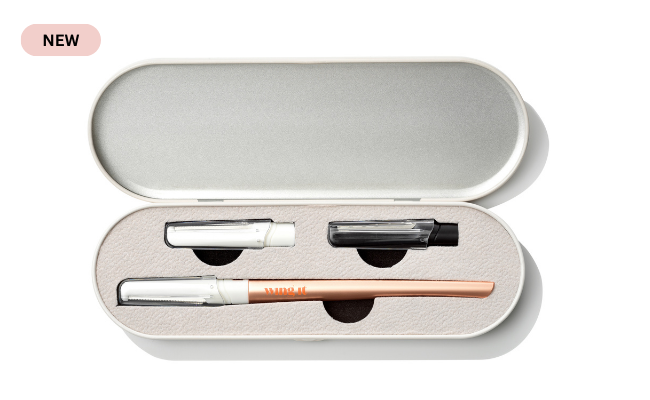
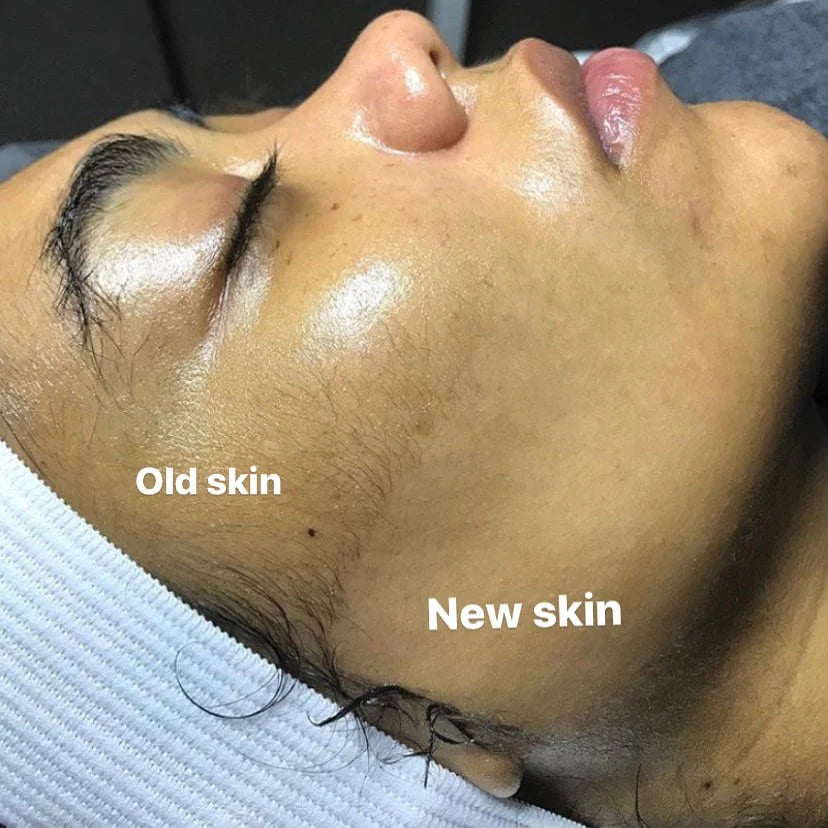
One of the best ways to slow down the visible signs of ageing is by adopting a consistent skincare routine that includes exfoliation. Dermaplaning is a gentle exfoliation method that involves using a small, sterile blade to remove dead skin cells and peach fuzz from the skin's surface. This treatment can be done professionally or at home using tools like the Forever Dermaplaning Razor.

Here are five reasons why dermaplaning at home can be your ultimate anti-ageing secret:
-
Boosts Collagen Production: Exfoliation through dermaplaning stimulates the skin’s renewal process, encouraging the production of new cells. This increased cell turnover helps to boost collagen production, keeping the skin firm and reducing the appearance of fine lines.
-
Improves Skin Texture: Dermaplaning removes the top layer of dead skin cells, revealing smoother, brighter skin underneath. This improved texture can help diminish the appearance of wrinkles and give the skin a youthful glow.
-
Enhances Product Absorption: Removing the dead cells and peach fuzz allows serums and creams to penetrate deeper into the skin, making them more effective. By following dermaplaning with a nourishing serum like the Collagen Fix Serum, you can deliver anti-ageing ingredients like peptides and hyaluronic acid more effectively to the skin.
-
Reduces the Appearance of Fine Lines: As dermaplaning helps to remove dead skin cells and stimulate collagen, it can reduce the appearance of fine lines, particularly around the eyes and mouth.
-
Increases Radiance: By removing dead cells and promoting cell regeneration, dermaplaning leaves the skin looking fresh and radiant. This can help counteract the dullness often associated with ageing skin.
Skin aging is a complex process influenced by both intrinsic and extrinsic factors. While we cannot stop time, we can certainly slow down the visible signs of ageing by understanding how the skin ages and taking steps to protect it. Regular exfoliation, such as dermaplaning at home, can be a game-changing addition to your skincare routine, promoting smoother, more youthful-looking skin.







1 comment
I was a scam victim, I lost a lot of money up to $170,000 I would like to express my gratitude to Innovations recovery Analyst for their exceptional assistance in recovering my funds from a forex broker. Their expertise and professionalism in navigating the complex process were truly commendable. Through their guidance and relentless efforts, I was able to successfully recover my funds of $170,000, providing me with much-needed relief. I highly recommend them on – INNOVATIONSANALYST@ GMAIL. COM to anyone facing similar challenges, as their dedication and commitment to helping clients are truly impressive. Grateful for their invaluable support in resolving this matter.
melissa levy
Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.